INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROMONITORING
Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM) uses electrophysiological signals such as Electroencephalography (EEG), Electromyography (EMG), and Evoked Potentials (EPs) to monitor the functional integrity of neural structures (nerves, spinal cord and parts of the brain) during surgery. The set of modalities used in a surgery depends on which neural structures are at risk.
The purpose of IONM is to reduce the risk to the patient of iatrogenic damage to the nervous system causing neurological deficits, such as muscle weakness, loss of sensation and impairment of normal bodily functions. IONM also delivers the surgical team with real time information, allowing surgical decision making and providing functional guidance.
IONM is fast being accepted as a standard of care for improving patient safety and surgical outcomes as IONM minimizes the risk of postoperative neurological deficits that may otherwise go undetected.
| SPECIALITY | PROCEDURE | EMG | T-EMG | SCREW | SSEP | MEP | D-WAVE | EEG | BAEP | VEP | ECOG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPINE | Scoliosis Correction | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Spinal Tumor Resection | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| De-tethering of cord | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Cervical/Thoracic Fusion | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Lumbosacral Decompression / Fusion | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Cauda Equina Surgery | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Sacro-iliac Fracture Reduction | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Spinal Surgery | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| ORTHOPAEDIC | Acetabular Fractures and Revision | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Total Hip (Revision,Limb Lengthening) | √ | √ | |||||||||
| NEUROSURGERY | Brain Tumors | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Skull Base surgeries with retraction | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Epilepsy Surgery | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Acoustic Neuroma Resection | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Vestibular Nerve Resection | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| Microvascular Decompression | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Carotid Endarterectomy | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Cerebral Aneurysm Clipping/Coiling | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Arteriovenous Malformations | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Transsphenoidal Pituitary Tumor | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm | √ | √ | |||||||||
| ENT | Parotidectomy | √ | √ | ||||||||
| Thyroidectomy | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Cochlear Implant | √ | ||||||||||
| PERIPHERAL NERVE | Brachial Plexus | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Nerve Root Avulsion | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Neuroma Incontinuity | √ | √ | √ |
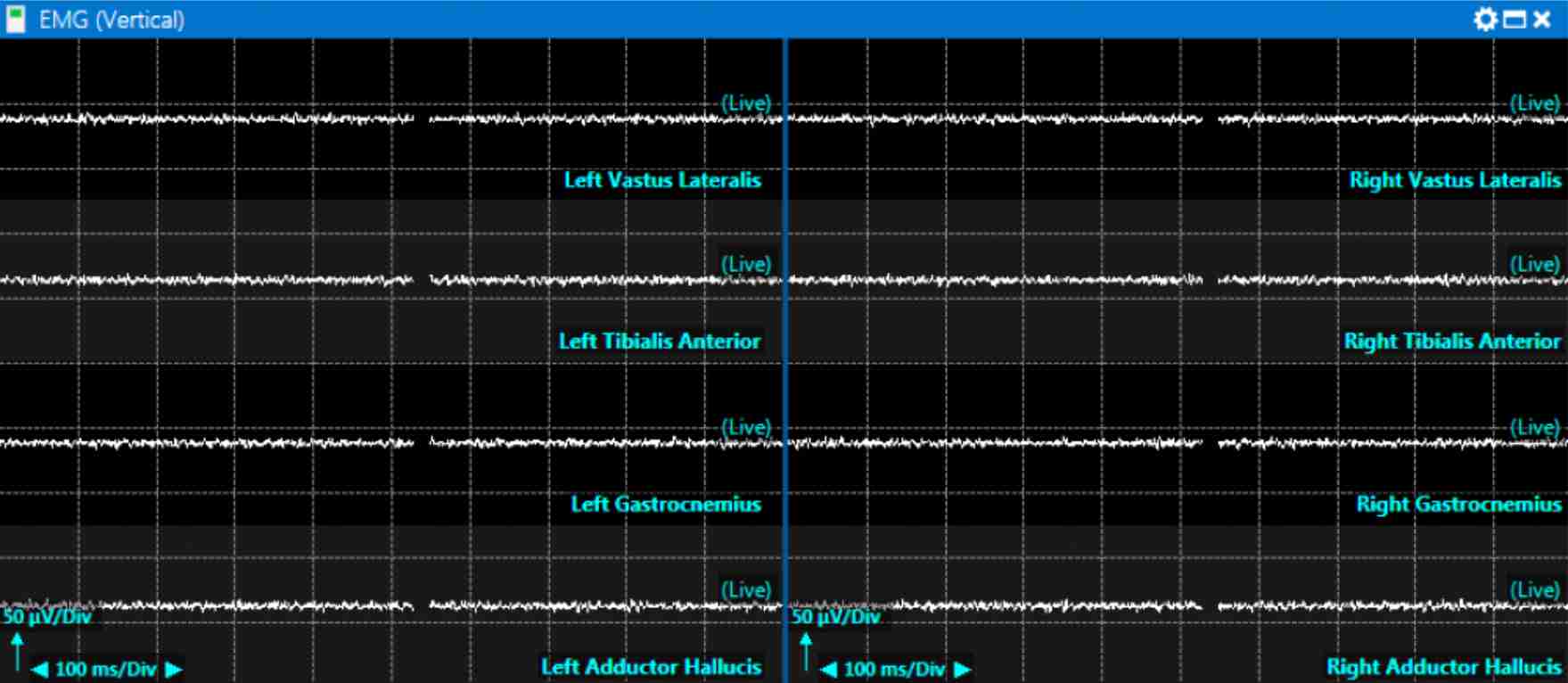
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG)
EMG
Electromyography is the recording of electrical activity of muscle tissue to monitor inadvertent damage to corresponding nerve
TEMG
Triggered EMG Allows electrical stimulation in the operative field to identify nerves in proximity & evaluation of patency of nerve by direct stimulation of the nerve
Threshold EMG / Screw Test
Confirmation of correct placement of pedicle screws during spine surgery using electrical stimulation at the screw head
ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG)
EEG
Electroencephalography is used to evaluate electrical activity in the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp.
ECoG
Electrocorticography uses electrodes placed directly on the exposed surface of the brain to record electrical activity from the cerebral cortex

EVOKED POTENTIAL (EP)
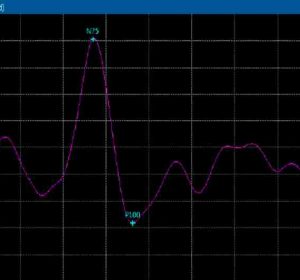
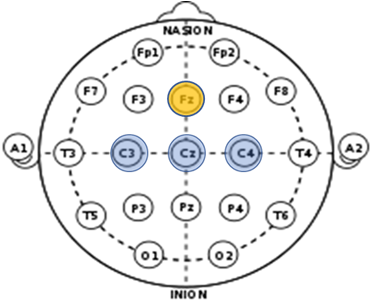
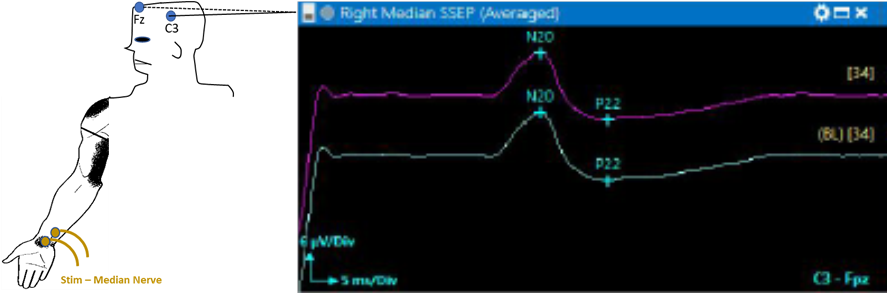
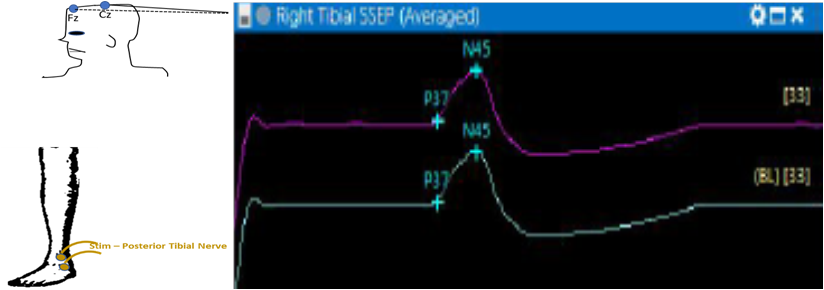
SSEP/SEP
Somatosensory/Sensory Evoked Potential provides information on the posterior sensory pathway by stimulation of peripheral nerves and evaluating response from the sensory cortex in the brain

EVOKED POTENTIAL (EP)
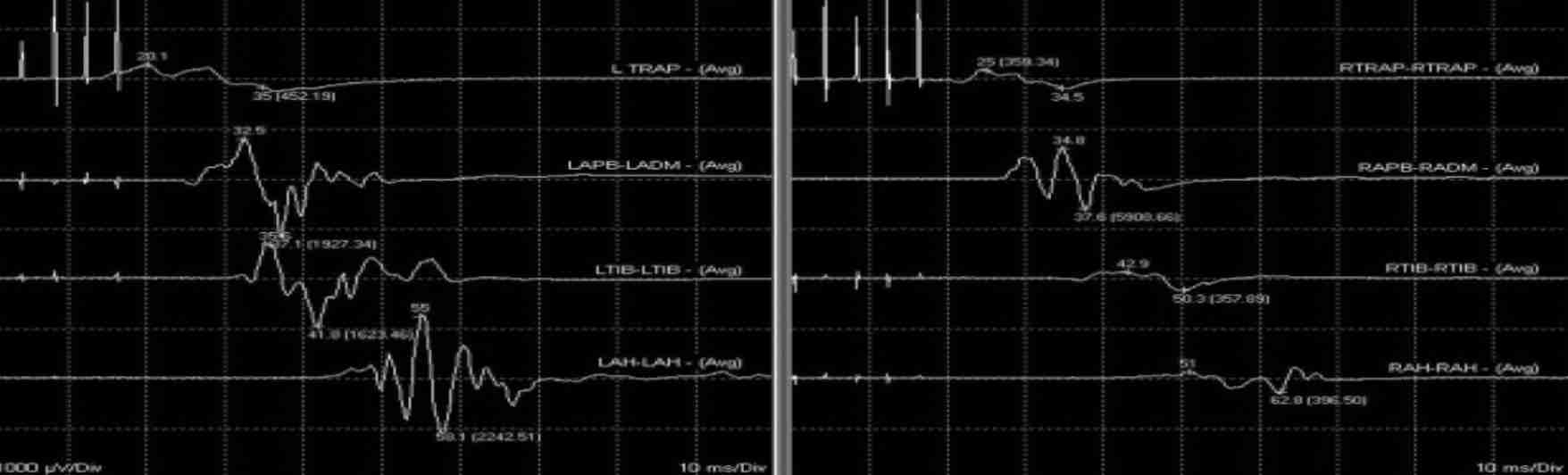
TCeMEP
Transcranial Electric Motor Evoked Potential provides information on the anterior motor pathway by stimulation of the motor cortex in the brain and evaluating response from relevant muscles in the body
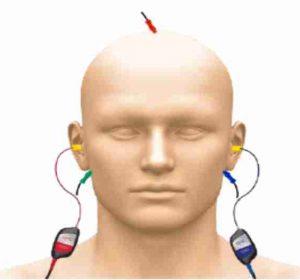
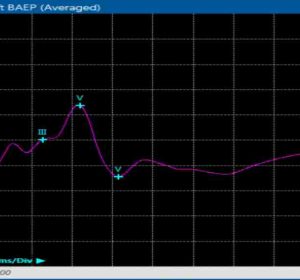
BAEP
Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potential allows evaluation of the neuronal activity in the auditory system
VEP
Visual Evoked Potential evaluates patency of the visual pathway by measuring the electrical signal generated at the visual cortex using visual stimulation